 OSI is the Open System Interconnection reference model for communications. The OSI model is mainly used as a point of reference for discussing other protocol specifications such as TCP/IP and Net Ware.
OSI is the Open System Interconnection reference model for communications. The OSI model is mainly used as a point of reference for discussing other protocol specifications such as TCP/IP and Net Ware.
The OSI reference model consists of seven layers that each defines a set of typical networking functions. The upper layers (application, presentation, and session; or Layers 7, 6, and 5) define functions focused on the application. The lower four layers (transport, network, data link, and physical; or Layers 4, 3, 2, and 1) define functions focused on end-to-end delivery of the data. Layer 2 is where switching is based, while Layer 3 is where routing is based.
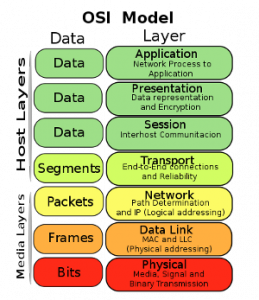
Here are example protocols for eachlayer:
- (7) Application – Telnet, HTTP, FTP, WWW browsers, NFS, SMTP gateways (Eudora, CC:mail, SNMP
- (6) Presentation – JPEG, ASCII, EBCDIC, TIFF, GIF, PICT, encryption, MPEG, MIDI
- (5) Session – RPC, SQL, NFS, NetBIOS , SSH, DECnet SCP
- (4) Transport – TCP, UDP, SPX
- (3) Network – IP, IPX, AppleTalk DDP
- (2) Data Link – IEEE 802.3/802.2, HDLC, Frame Relay, PPP, FDDI, ATM, IEEE 802.5/802.2
- (1) Physical – EIA/TIA-232, V.35, EIA/TIA-449, RJ-45, Ethernet, 802.3, 802.5, B8ZS

Leave a Reply